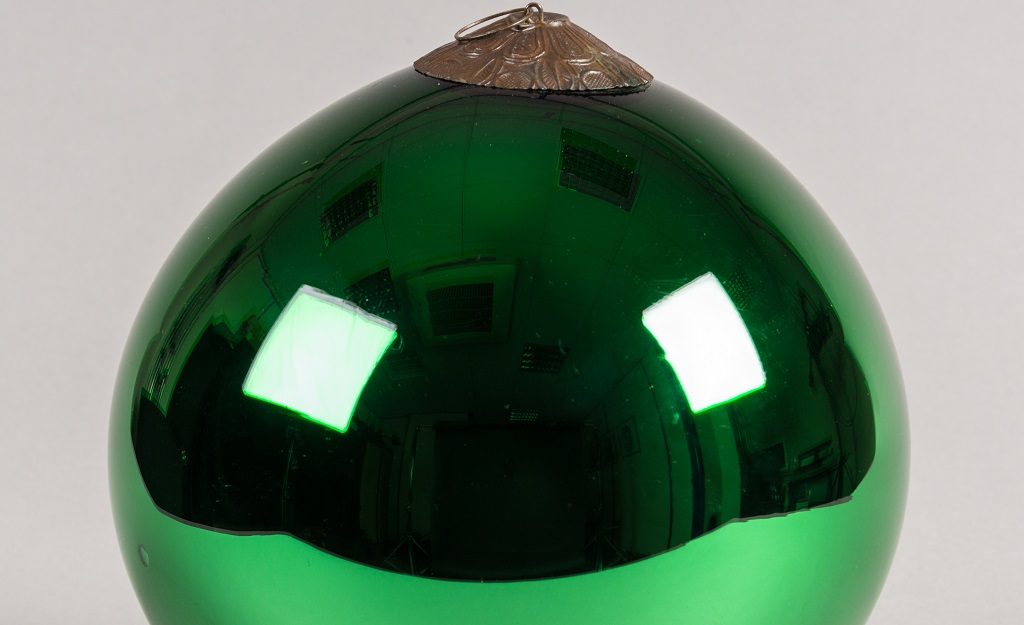
I will never forget my first encounter with a witch’s ball. I was cataloguing and documenting the collection at Historic Environment Scotland when I came across it. I soon developed a fascination for the green glass sphere that looked like a big Christmas bauble.
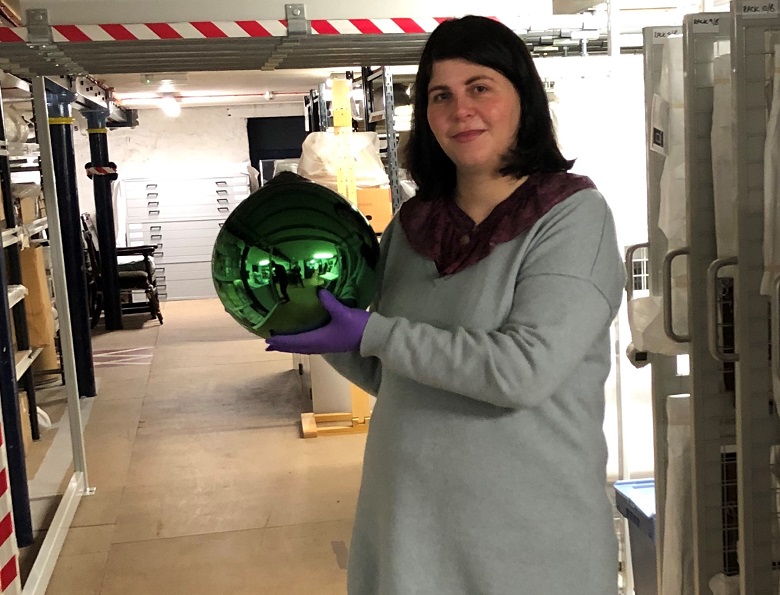

Careful you don’t drop it! Chiara examines the Witch’s Ball in the HES collection.
The copper alloy fitting and loop on top of it served the purpose of hanging it, but not onto trees! Objects of this kind are usually associated with dark magic and have been used for the protection of the household since the 17th century. The superstition and general practice consists in hanging them next to the windows to ward off evil spirits. But what is the meaning of this tradition and where does it come from?
The origins of witch’s balls
There is more than one answer to this question as witch’s balls have served many different purposes over time. However, their popularity as apotropaic* objects begins in the 17th century, runs through the 18th and 19th century and it is still very much alive today.
(* We had to look it up too! Apotropaic refers to an object supposedly having the power to avert evil influences or bad luck.)
1: A Fisher Wives’ Superstition
The belief is likely to originate in the fishermen communities. Sailors’ wives hung a glass float in a window in the hope that it would protect their husbands at sea.
It is possible that the connotation with witchcraft derives from the late 17th century witch trials. It is possible that the connotation with witchcraft derives from the late 17th century witch trials. In some European countries there was a practice of trying suspected witches by binding their arms and legs and throwing them into water. If the woman floated, she was a witch. By resemblance, the hallow glass buoys attached to the edges of fishing nets to keep them afloat have been associated with witchcraft trials. Although ‘ducking’ wasn’t a common practice in Scotland, people in Scotland may well have been aware of the superstitious link between buoyancy and witchcraft.
Many maritime museums have witch’s balls in their collections. When strolling through fishermen villages it is still possible to see glass baubles hanging in cottages windows.
Pittenweem is a typical Scottish fishing village. Wives here may have used glass floats as good luck charms.
2: Witch’s Bottles
The practice of using stoneware bottles for the protection of the household dates to the 17th century. Witch’s bottles were usually buried at the entrance of the house and were filled with contents of various nature. Iron pins or nails, human hair, bones, thorns, pieces of wood, fabric and urine were all typical components. These ingredients acted as spells or counter-spell against witchcraft.
3: Watch Balls
In the early 18th century, pretty toys were hung up in nurseries to catch a child’s eye. These were called ‘watch balls’ and were possibly intended for the protection of children from malevolent spirits. With time, their name was corrupted into witch ball. This caused immediate association of these toys with superstitions of witches and evil eye.
Our witch’s ball
How did the witch’s ball come to be in the HES collection?
Some investigation reveals its provenance. We know that the object was first recorded as part of a collection assembled by Jane (1860 – 1937) and Louisa (1858 – 1949) Macdonald , who were prominent figures in the town of Arbroath. The sisters helped to establish a local history museum in the Abbot’s House at Arbroath Abbey.
Of the two sisters, it was Jane who was most devoted to the museum at the Abbot’s house. Her obituary paints a picture of a woman who “possessed a vivid personality, joined with a cultured mind and a wide outlook.” She was a well-known personality in Angus and a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries Scotland. Her knowledge of antiquarian subjects was vital when it came to piecing together the collection at the Abbott’s House, where she was in charge of making decisions about which objects should be included.
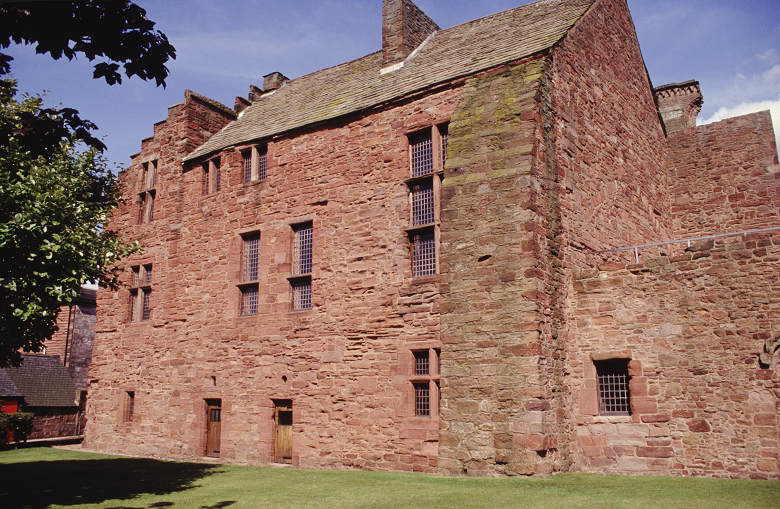

The Abbot’s House at Arbroath Abbey. The Macdonald sisters donated their collection to the museum here.
After Jane’s passing in 1937, this collection was donated to Abbot’s House by her younger sister Louisa MacDonald. The Abbot’s House had been acquired by a predecessor of HES in 1924, and this is how the ball eventually came to be in our care.
However, there’s lots we still don’t know about this object. For instance, how old is it? Last December it was possible to establish the date of this object through analysis of the glass, for the first time. This is an important breakthrough in understanding the witch’s ball and its use.
Investigating the witch’s ball
Two members of staff within HES science team, Dr Maureen Young and Aurélie Turmel, carried out the analysis. They used a portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. This technology permits to obtain information on the chemical composition of a range of materials without damaging the objects.
In this case, different calibration of the equipment was necessary to pick up the presence of both heavy and light elements. During the analysis it was also necessary to keep the object in its storage box because of its round shape.
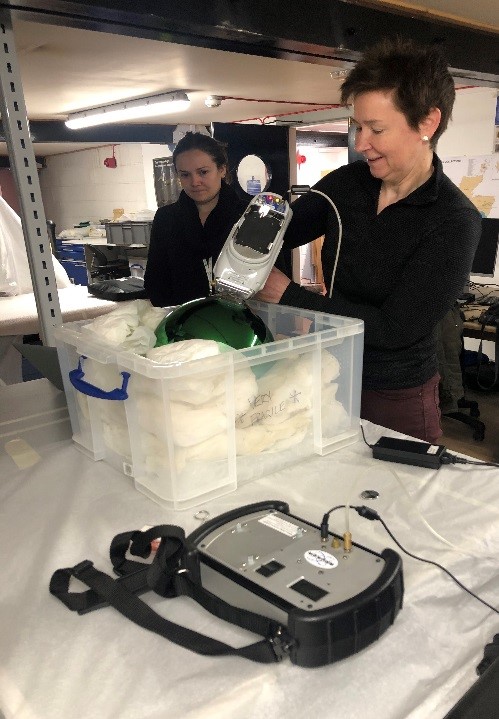

Dr Maureen Young and Aurélie Turmel using xrf portable equipment to analyse the witch’s ball.
The range of components present in the glass permitted to assign a time of production for the witch’s ball. A peak in the presence of arsenic suggests that this object may be dated in-between 1835-1870.
However, the high level of pigmentation additives such as chromium, iron and copper strongly points to the 20th century as possible date of production.
Modern mystics
As a Victorian object, this witch’s ball was not only a magical object. It could also have been used in the dining room to help the service or in the front yard to see calling visitors. It is worth noticing that glass was an expensive material and a commodity in affluent homes at the time. Objects of this kind show superstitions of witches and evil eye were very much alive in the Victorian period. Witch’s balls had a steady market, being manufactured in many different sizes.

Alloa Glass work with staff showing their work in 1897. Witch’s balls of different sizes are among the many objects produced at the factory.
© Courtesy of The National Museums of Scotland.
As a 20th century object, this witch’s ball might have been simply used to decorate a house interior. But who knows what beliefs the owner might have held. Perhaps they still wanted protection from the evil eye.
Gazing into the witch’s ball
Although it’s not all that old, the witch’s ball is incredibly fragile so we keep this little piece of history tucked away safe in our collections. It’s not kept in storage because we’re scared of summoning something, honest!

